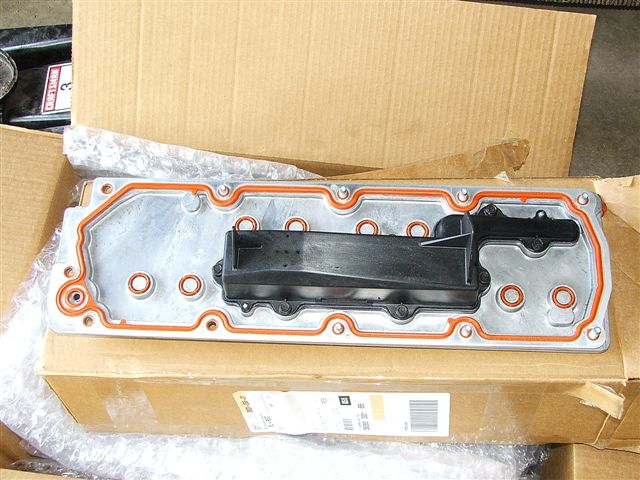
DOD Delete or Displacement on Demand, also known as AFM, is a fuel management approach for large displacement gasoline engines. The goal is to decrease the number of cylinders burning fuel during light engine load to improve the fuel economy. Unfortunately, DOD systems led to several engine issues, including wear, increased oil consumption and even jerking during acceleration.
Table of Contents
Hence, DOD or AFM delete approaches were introduced to rectify the issues. AFM delete has been beneficial for high mileage engines, especially because of the reduced maintenance concerns. However, it does lead to higher emissions.
What Is DOD
Displacement on Demand or cylinder deactivation is a system where the engine stops a few cylinders from operating during low engine load for fuel economy reasons. The engine control module or the ECM turns the injectors off for the cylinders simultaneously. Their intake valves which draw the air in also cease along with the exhaust valves. The pistons for these deactivated cylinders may keep going up and down because they are attached to the spinning crankshaft but it's just going along for the ride, at that point.
DOD systems are problematic, however, as they are susceptible to carbon contamination, among other things. Similarly, during DOD activation, the lifters' internals only have the oil during activation, which can be taxing on the engine. For this reason, vehicles with DOD only run successfully when their engines are maintained regularly and with the right oil.
What Is AFM
Displacement on demand and Active fuel management is essentially the same thing. The trademarked technology by General Motors was created to reduce gas mileage of both V6 and V8 engines. It works by shutting off half of the engine cylinders to operate at a reduced power level during cruise or low load situations. They did improve fuel economy but also increased the complexity of the engine management system. AFM also affected the overall engine durability, which is a highlight of LS powertrains. With AFM, the higher mileage engines have a higher tendency to fail, considering the system shuts off the same cylinders each time it is activated.
The AFM activation and deactivation is controlled by the Valve Lifter Oil Manifold or VLOM. It has four solenoids and is positioned on top of the engine block below the intake manifold. The VLOM directs the flow of pressurized oil to the AFM as well as the exhaust valve lifters. Pressurized oil is applied to the DOD lifters during cylinder deactivation. The activation and deactivation of the cylinders happens on the base circle of the cam lobe, allowing for a smooth transition that is unnoticeable when driving.
What Does A DOD Delete On An LS Engine Mean?
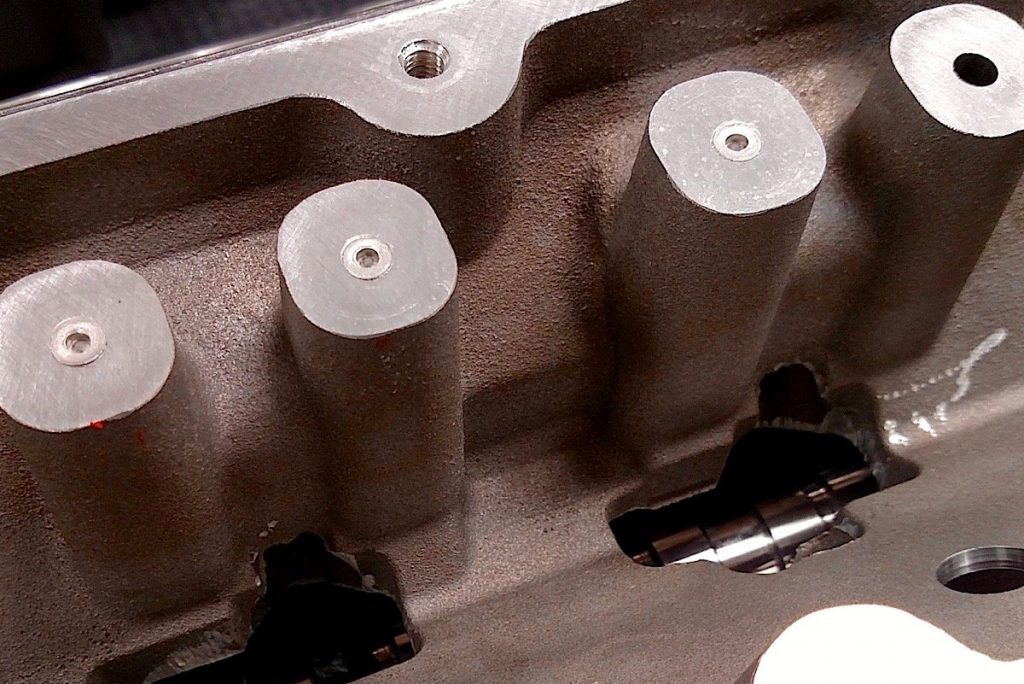
Removing the active fuel management system is known as the DOD delete, which is fairly common because the system leads to long term problems. These include high oil consumption and loss of power. LS engines are generally designed to be durable so the AFM can be counterproductive to this attribute. A delete kit will require a fair bit of internal work on the engine, though, entailing new lifters, pushrods, DOD delete plugs and valve springs. The DOD delete procedure is usually the same for all generation four LS engines though there are more steps if it has variable valve timing.
Following the replacement of the AFM equipment, the VLOM should be modified, so it does not initiate Active fuel Management. Alternatively, the other 5.3 cylinder deactivation delete approach would be a Range tuner disabler. The Range device turns off AFM, but the Engine Control Module sometimes tries to activate it, even with a VLOM delete. That deactivates the cylinders without having to change the components. It is the most accessible and convenient alternative; however, it is not legal in every state.
Why Are DOD Lifters Different?
Engines that use AFM systems have special lifters for their cylinders. They are taller compared to regular lifters and have special holes for oil. The DOD lobes also have more lift and duration compared to the non-DOD lobes. It is because the DOD lifters tend to bleed more oil compared to the non-DOD lifters.
The leakage reduces the lift and duration of the cam. This oil loss also happens with standard lifters but at a lower level. That is why DOD engines utilize high volume oil pumps.
DOD Delete Pros And Cons
Pros
An AFM delete can be a practical solution for LS engines as it prevents spending on DOD related repairs. The system is not only a good thing for the sake of preventive maintenance, but it also keeps the car in V8 mode. Luxury Sport engines were made to provide a lot of power and acceleration so an AFM delete would make that delivery unhindered. AFM lifter failure sometimes causes the vehicle to jerk when accelerating without warning, so removing AFM should improve overall safety of the driver and occupants. As mentioned, DOD systems increase general oil consumption.
The removal AFM and replacing the DOD lifters with standard ones should reduce overall oil and other maintenance needs. AFM also impacts the general durability of the engine, so a Chevy DOD delete, for example, should reduce the wear and tear effects for high mileage vehicles. Lastly, GM DOD systems cause an annoying exhaust drone within the cab during low power modes. An AFM delete should improve the noise situation.
Cons
The AFM delete will revert gas mileage to the original settings as all cylinders will be in operation. That means less fuel economy and increased emission levels. Unfortunately, DOD deletes may also result in the engine running hotter and that could lead to carbon build up on the cylinder walls or lifters. That could potentially lead to engine knocks. Oddly, AFM delete may also cause loss of power and hesitation.
The engine utilizes all cylinders even when maximum power is not needed. The engine will then have to work harder, resulting in deterioration over time and reducing overall capability.
How To Fix The AFM Delete Issues
AFM delete is increasingly becoming popular, especially in the higher mileage vehicles, as users realize rapidly reducing benefits of DOD. It is also recommended for individuals that want to install performance upgrades. However, the DOD delete also comes with several problems. For example, the check engine light may come on after the delete. The probable reason for this is a complex emission control system. The AFM delete will cause the car to have more emissions, triggering the warning. In this case, it may be a good idea to take it to the mechanic to sort the issue.
AFM delete also leads to more strain on the engine due to the replacement of parts. It is also from the constant use of all cylinders. One answer to this would be to install a tuner, or DOD delete programmer as they can disable the DOD without requiring the same changes to the hardware.
Conclusion
AFM systems were created with good intentions at heart as they reduced the overall fuel economy and emissions for large capacity GM engines. Over time, they became more trouble than they were worth, which is why DOD delete is a common solution. Hitting the reset button on the engine operation will bring back perpetual V8 mode while improving oil use. There are drawbacks, though.
It is a hassle for those who prefer the delete kit over the Range Tuner, and there are potential maintenance issues. Regardless, AFM delete remains one of the solid ways of dealing with DOD problems.


